「人より勉強に時間がかかる」と感じていませんか?
私の学校にも、同じ悩みを抱えて苦しんでる生徒がたくさんいます。
• 「教科書や参考書の内容がわからなくて、読むのに時間がかかる」
• 「解答の意味が理解できず、勉強が進まない」
教科書や参考書の内容を理解するには、「自分なりに噛み砕いて考える力」が必要です。
でも大丈夫!
このサイトでは、私が受けた質問や、つまずきポイントをもとに、わかりやすく解説していきます。
「噛み砕き方」がわかれば、文章はぐっと読みやすくなります!
三角比:まとめページ
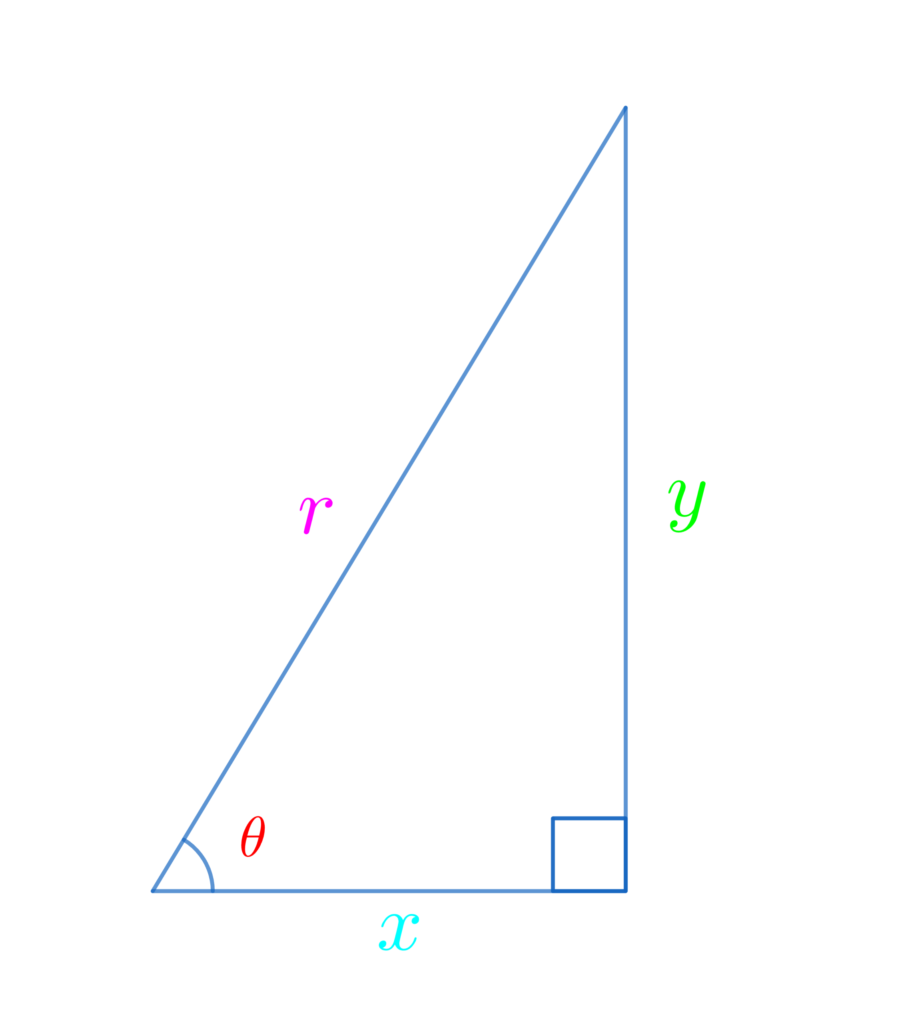
三角比01:直角三角形を用いた三角比の定義

まずは、直角三角形を使った三角比の定義を覚えましょう!
\(\displaystyle\color{red}{\sin{\theta}}=\frac{\color{lime}{対辺}}{\color{hotpink}{斜辺}}=\frac{\color{lime}{y}}{\color{hotpink}{r}}\)
\(\displaystyle\color{red}{\cos{\theta}}=\frac{\color{deepskyblue}{底辺}}{\color{hotpink}{斜辺}}=\frac{\color{deepskyblue}{x}}{\color{hotpink}{r}}\)
\(\displaystyle\color{red}{\tan{\theta}}=\frac{\color{lime}{対辺}}{\color{deepskyblue}{底辺}}=\frac{\color{lime}{y}}{\color{deepskyblue}{x}}\)
三角比02:有名角 30°, 45°, 60° の三角比

30°, 45°, 60° の三角比の値は暗記しましょう!

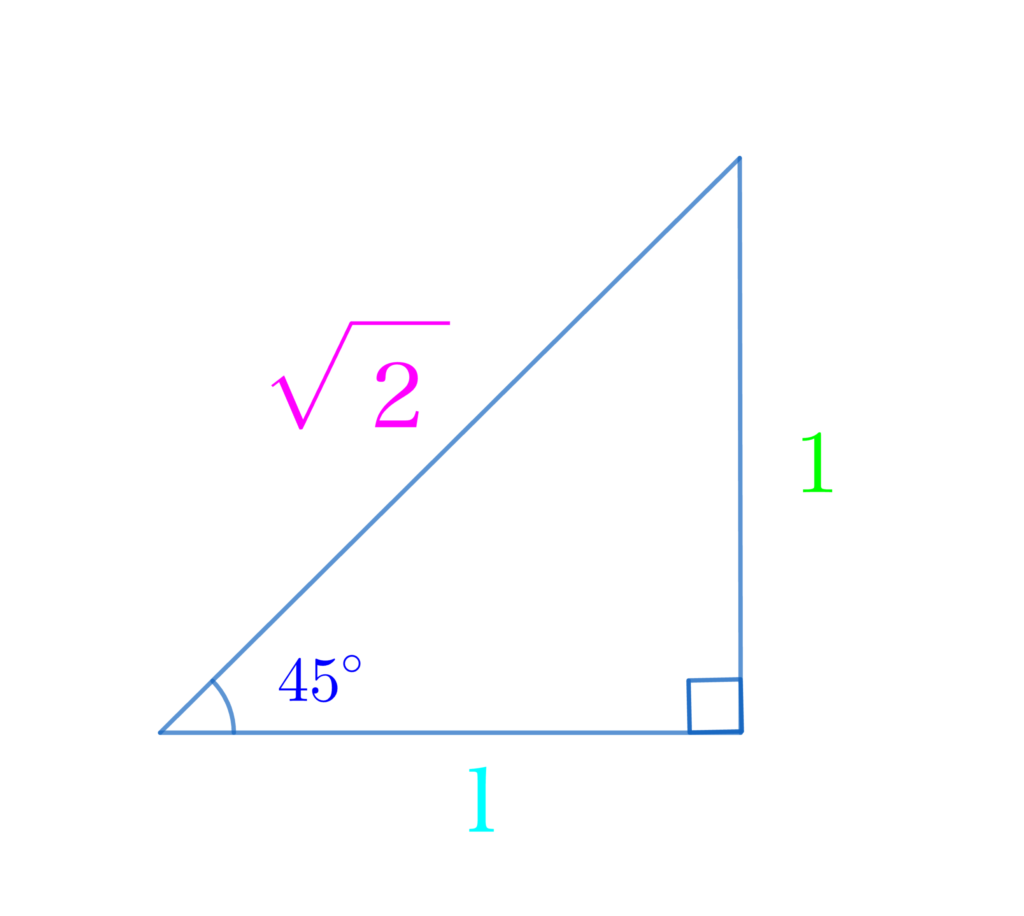

| θ | 30° | 45° | 60° |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(\sin{\theta}\) | \(\displaystyle\frac{1}{2}\) | \(\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) | \(\displaystyle\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) |
| \(\cos{\theta}\) | \(\displaystyle\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) | \(\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) | \(\displaystyle\frac{1}{2}\) |
| \(\tan{\theta}\) | \(\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) | \(1\) | \(\sqrt{3}\) |
三角比03:三角比による計測

三角比の定義を使って、直角三角形の辺の長さを求める方法を学びましょう!
水平線を基準にして上を見上げるときの角度のこと。
水平線を基準にして下を見下ろすときの角度のこと。
\(\color{red}{\sin{\theta}}=\frac{\color{lime}{y}}{\color{hotpink}{r}}\) より \(\color{lime}{y}=\color{hotpink}{r}\color{red}{\sin{\theta}}\)
\(\color{red}{\cos{\theta}}=\frac{\color{deepskyblue}{x}}{\color{hotpink}{r}}\) より \(\color{deepskyblue}{x}=\color{hotpink}{r}\color{red}{\cos{\theta}}\)
\(\color{red}{\tan{\theta}}=\frac{\color{lime}{y}}{\color{deepskyblue}{x}}\) より \(\color{lime}{y}=\color{deepskyblue}{x}\color{red}{\tan{\theta}}\)
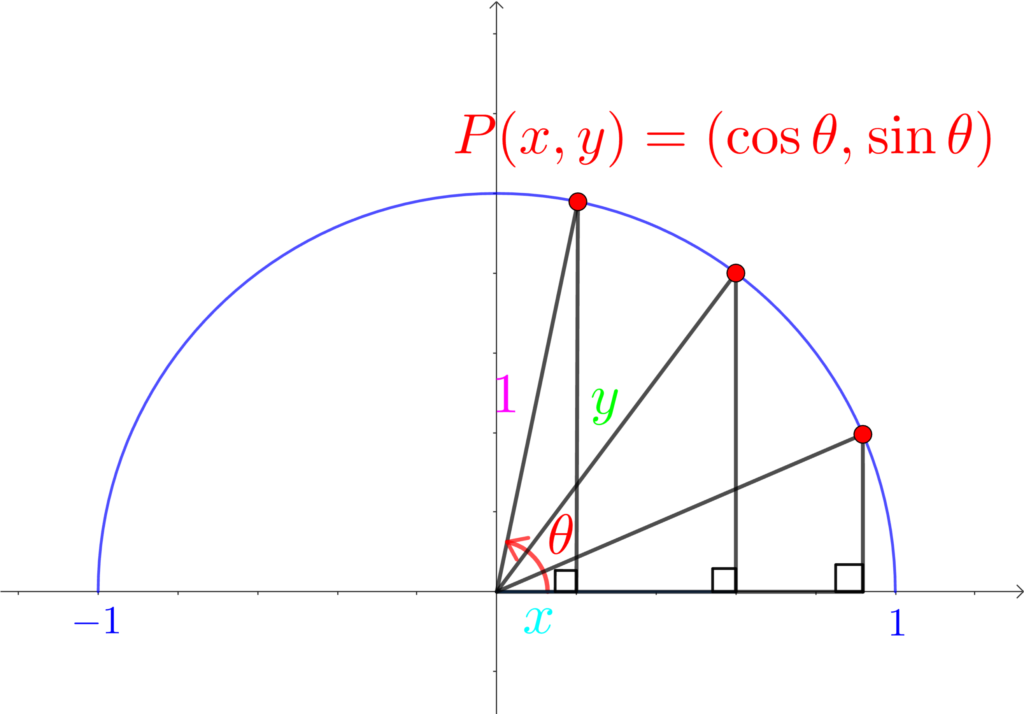
三角比04:単位円を用いた三角比の定義

直角三角形を使った定義は卒業!
これからは、単位円を使った定義を覚えましょう!
長さ\(1\)、\(x\) 軸方向からの回転角 \(\theta\) の線分と単位円の交点 \(P\) の座標が \((\cos{\theta}, \sin{\theta})\)
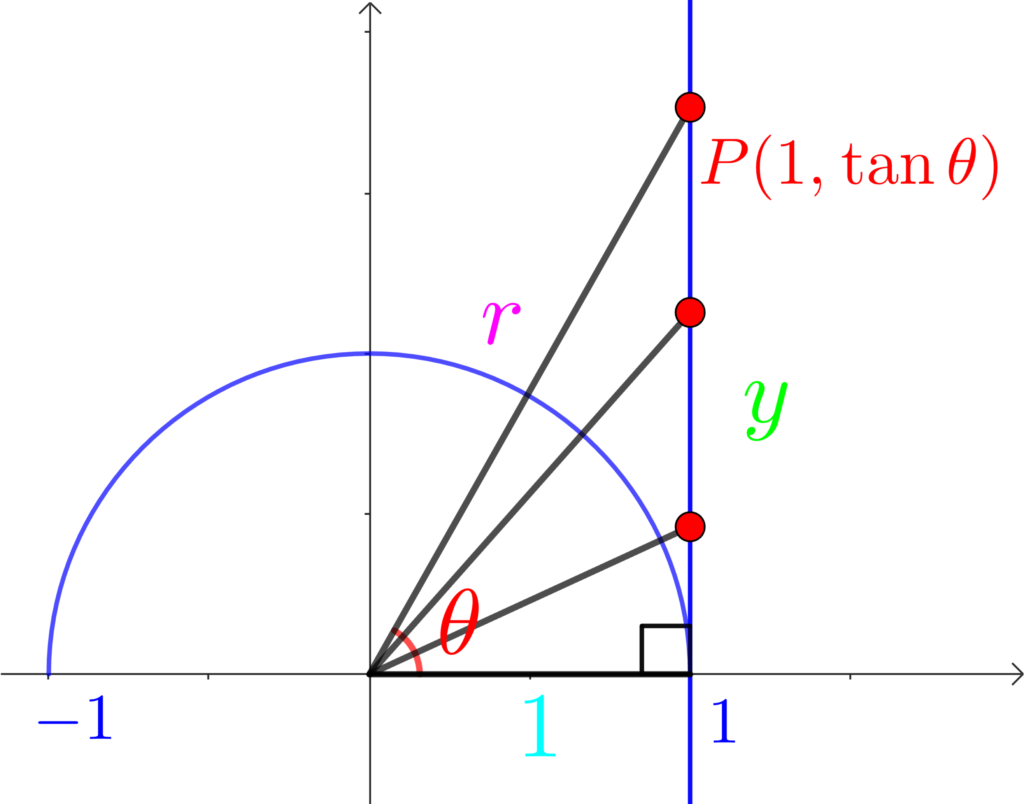
\(x\) 軸方向からの回転角 \(\theta\) の直線と直線 \(x=1\) との交点 \(P\) の\(y\) 座標が \(\tan{\theta}\)
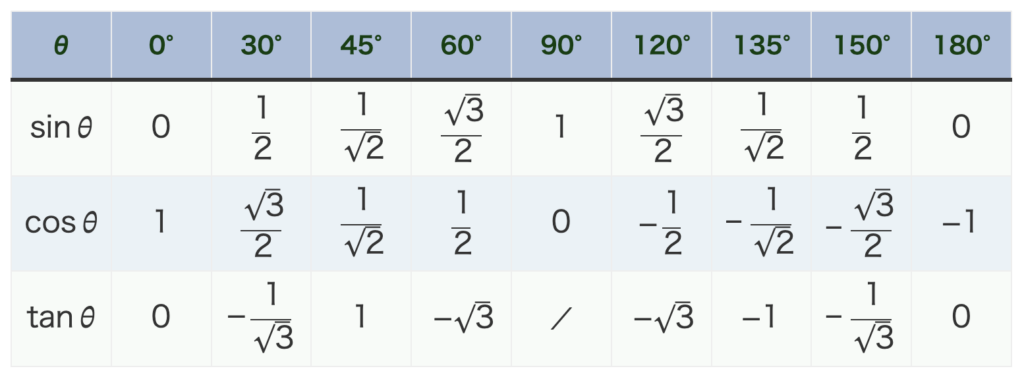
- 90°関連(0°, 90°, 180°)の三角比
→ 単位円で考える。(\(\sin{\theta}\) は \(y\) 座標、\(\cos{\theta}\)は \(x\) 座標 )
- 30°関連(30°, 60°, 120°, 150°)の三角比
→ 大きさは \(\frac{1}{2}=0.5\) or \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}≒0.9\) 。符号は単位円で考える。
- 45°関連(45°, 135°)の三角比
→ 大きさは \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) 。符号は単位円で考える。
- 90°関連(0°, 90°, 180°)の三角比
→ 単位円で考える。(\(\tan{\theta}\) は \(x=1\)の\(y\) 座標)
- 30°関連(30°, 60°, 120°, 150°)の三角比
→ 大きさは \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}≒0.6\) or \(\sqrt{3}≒1.7\) 。符号は単位円で考える。
- 45°関連(45°, 135°)の三角比
→ 大きさは \(1\) 。符号は単位円で考える。
三角比05:三角比を含む方程式の解き方

三角比の方程式を解く方法を詳しく解説!
- 範囲を確認する。
- 単位円を書く。
- \(\sin\) なら \(y\) 座標。\(\cos\) なら \(x\) 座標。\(\tan\) なら \(x=1\) の \(y\) 座標に値をとる。
- 角度を読み取る。
\(0°≦\theta≦180°\) のとき、\(\displaystyle\sin{\theta}=\frac{1}{2}\) を満たす \(\theta\) を求めよ。
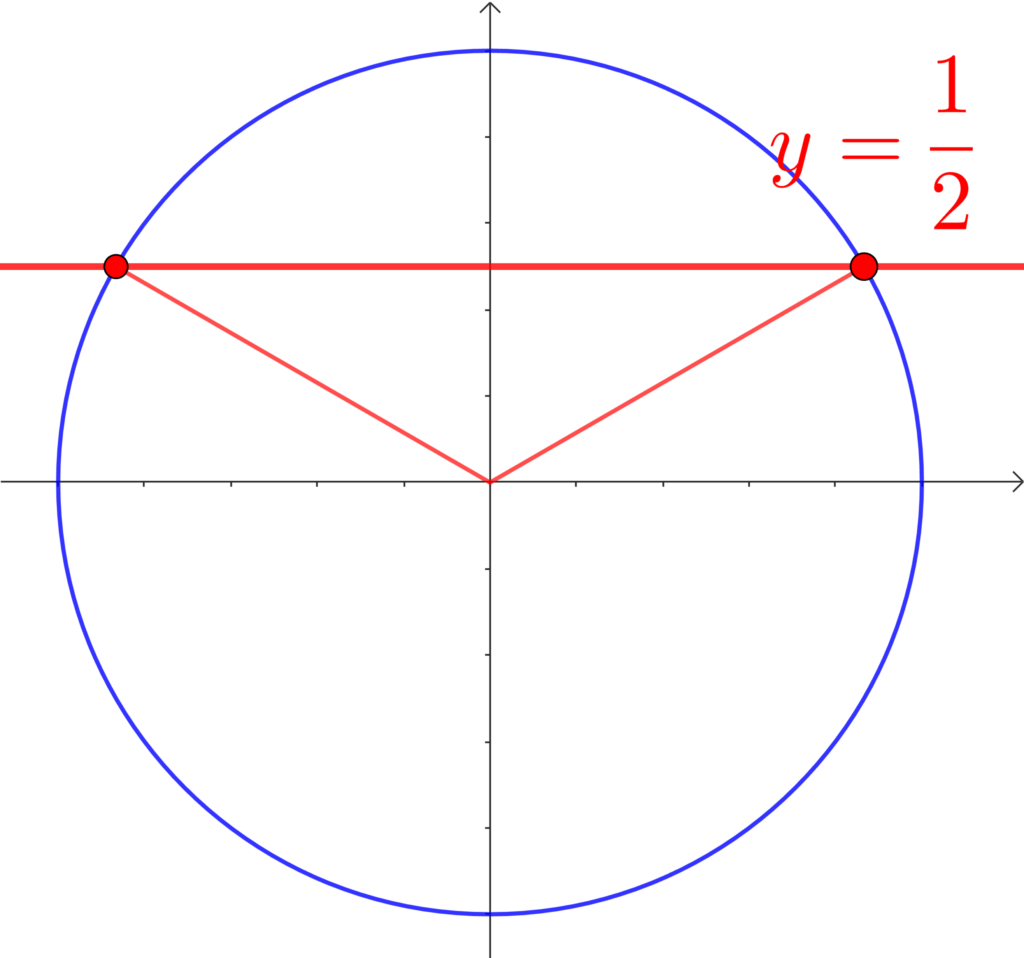
\(\theta=30°, 150°\)
\(0°≦\theta≦180°\) のとき、\(\displaystyle\cos{\theta}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) を満たす \(\theta\) を求めよ。
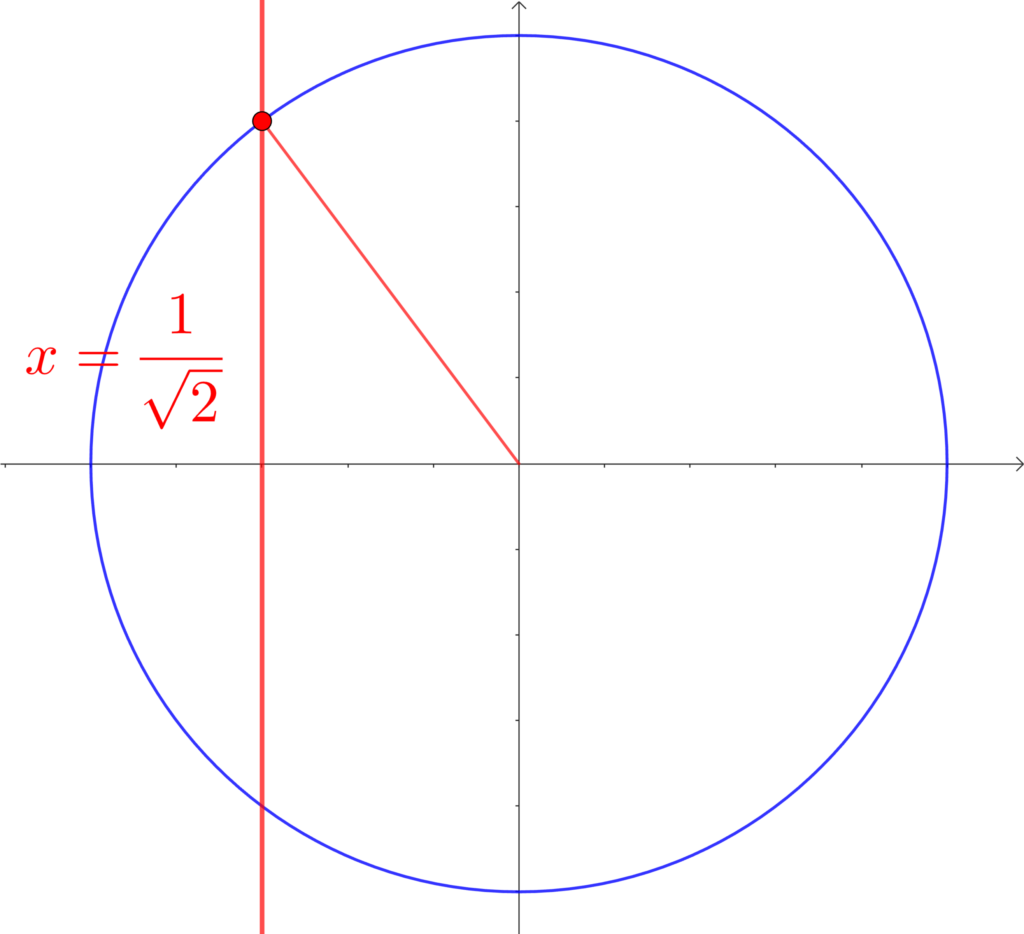
\(\theta=135°\)
三角比06:直線の傾きと tanθ

直線と \(x\) 軸のなす角の求め方を解説!
直線 \(y=mx\) と \(x\) 軸の正の向きとのなす角 \(\theta\) とすると \(m=\tan{\theta}\)
直線 \(y=\sqrt{3}x\) と \(x\) 軸の正の向きとのなす角 \(\theta\) を求めよ。
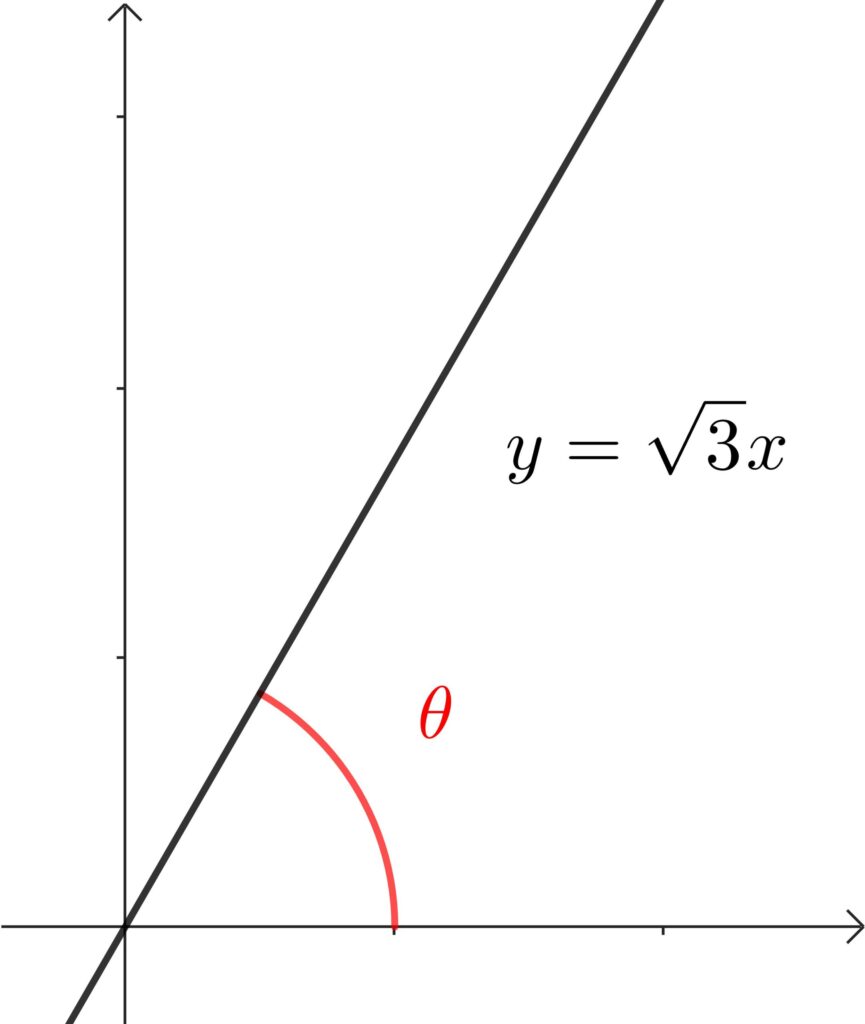
\(\tan{\theta}=\sqrt{3}\) より \(\theta=60°\)
三角比07:三角比の相互関係

① sin と cos と tan の関係式:\(\displaystyle\tan{\theta}=\frac{\sin{\theta}}{\cos{\theta}}\)
② sin と cos の関係式:\(\sin{^2}\theta+\cos{^2}\theta=1\)
③ cos と tan の関係性:\(\displaystyle 1+\tan{^2}\theta=\frac{1}{\cos{^2}\theta}\)
\(\theta\) は鋭角とする。\(\color{deepskyblue}{\sin\theta=\frac{2}{3}}\) のとき、\(\color{lime}{\cos\theta}\) と \(\color{hotpink}{\tan\theta}\) の値を求めよ。
\(\cos\theta>0\) より
三角比08:90°-θと180°-θの公式

① 関数の変化を考える
・90°のとき :\(\sin\) → \(\cos\)、\(\cos\) → \(\sin\)、\(\tan \)→ \(\frac{1}{\tan\theta}\)
・180°のとき:関数は変化しない
② ± を考える
・単位円を描き、鋭角のθで考えたときの ± と一致する
次の三角比を別の角の三角比で表せ。
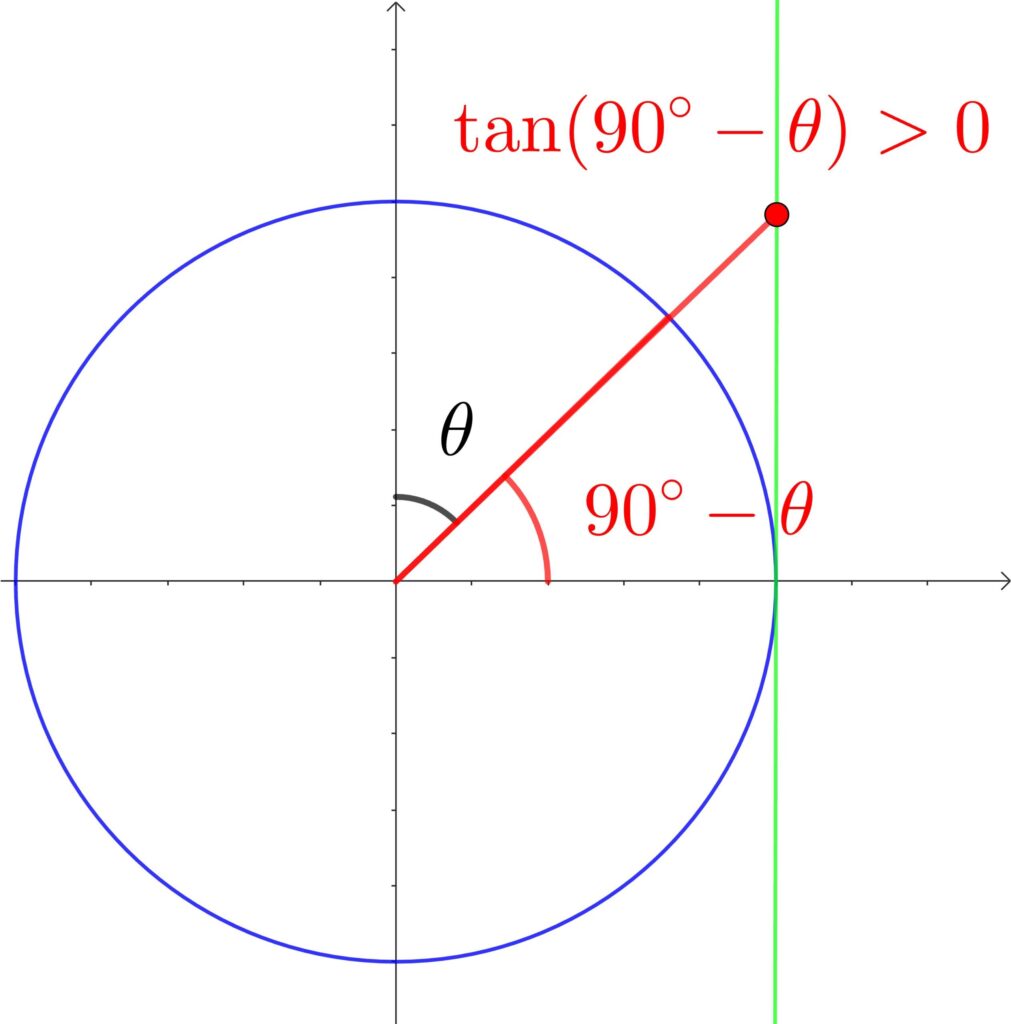
(1) \(\displaystyle\tan(90°-\theta)\)
(2) \(\cos(180°+\theta)\)
(1) \(\displaystyle\tan(90°-\theta)\)
① 90°なので \(\tan \)→ \(\frac{1}{\tan\theta}\)
② 単位円より符号は +
よって、\(\displaystyle\tan(90°-\theta)=\frac{1}{\tan\theta}\)
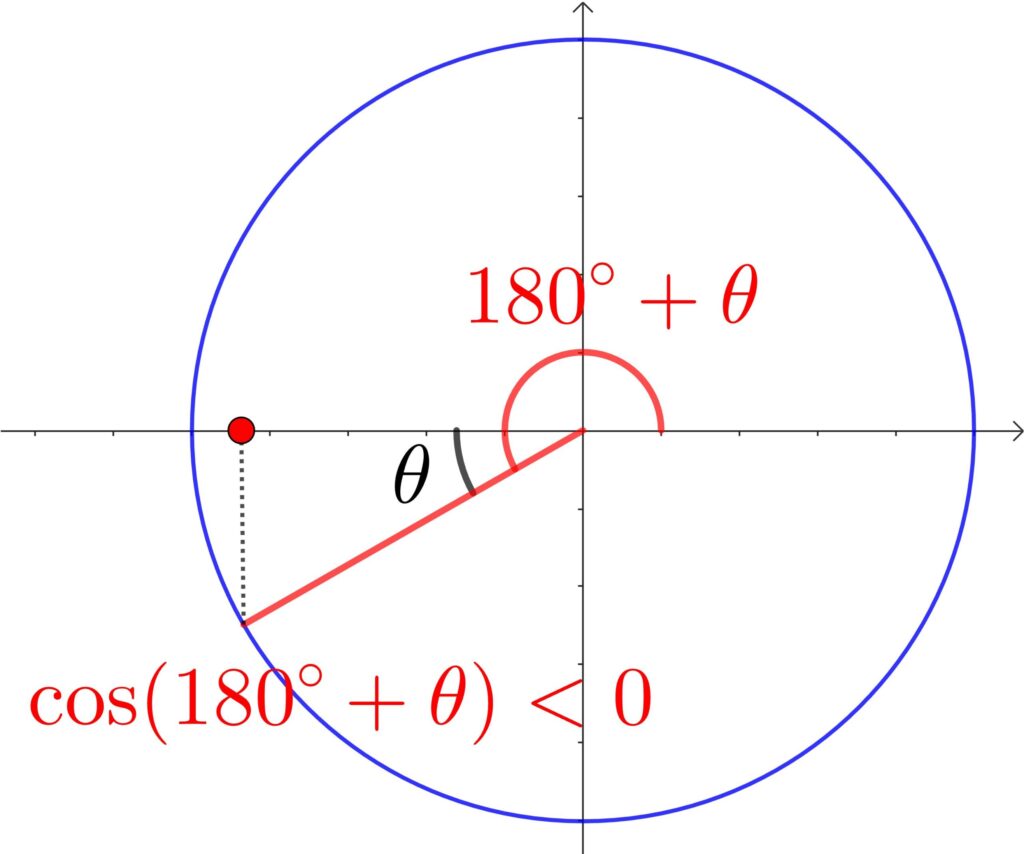
(2) \(\cos(180°+\theta)\)
① 180°なので関数の変化なし
② 単位円より符号は –
よって、\(\cos(180°+\theta)=-\cos\theta\)
三角比09:正弦定理

\(\displaystyle\frac{a}{\sin{A}}=\frac{b}{\sin{B}}=\frac{c}{\sin{C}}=2R\)
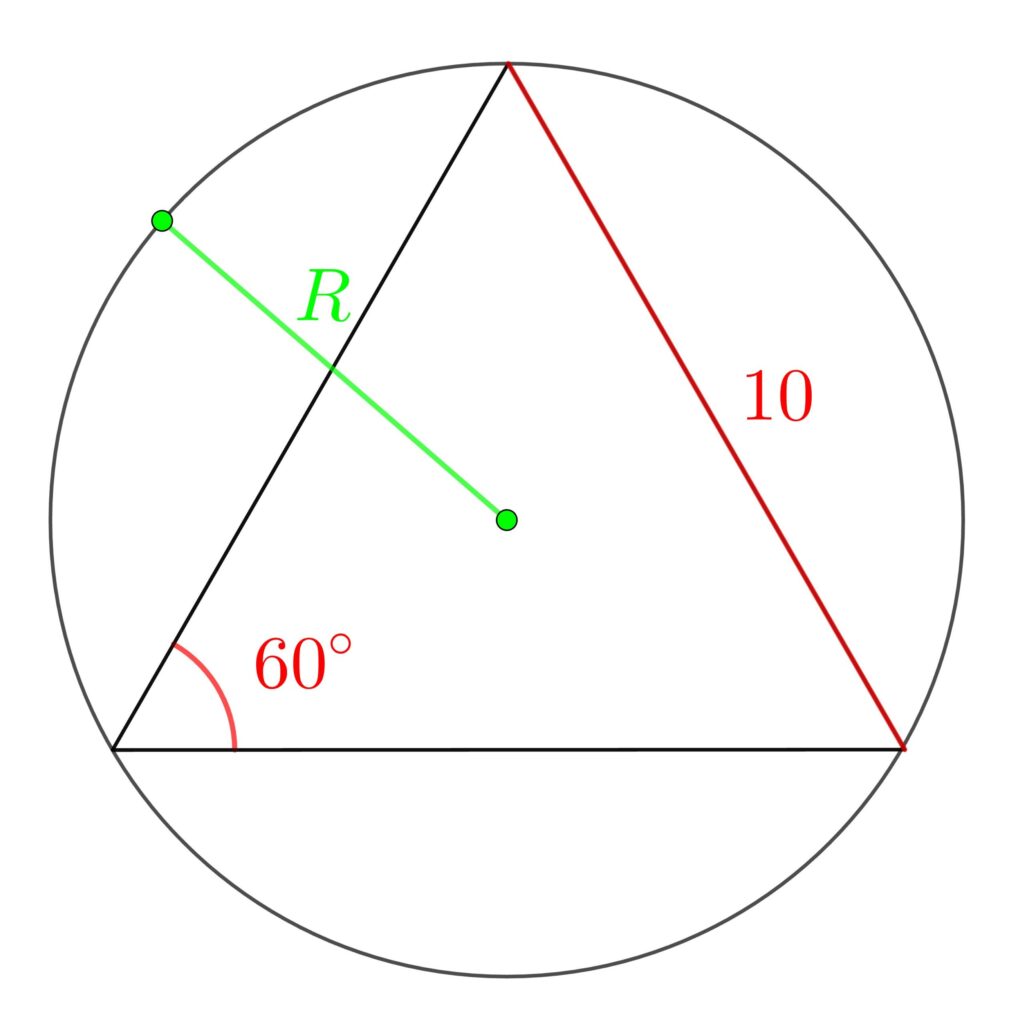
(1) 1辺の長さが10の正三角形ABCの外接円の半径Rを求めよ。
(1) 正弦定理より
\(\displaystyle\frac{10}{\sin{60°}}\) \(=\) \(\displaystyle 2R\)
よって
\(\displaystyle R=\frac{10}{\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\cdot2}=\frac{10}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{10\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
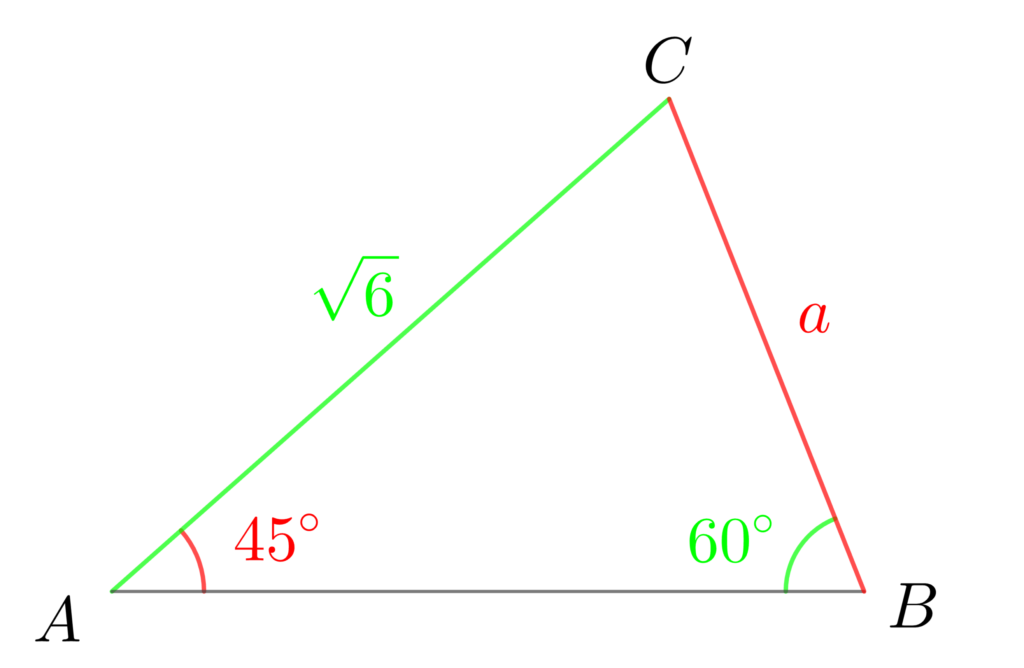
(2) △ABCにおいて、\(b=\sqrt{6}\) 、\(A=45°\)、\(B=60°\) のとき、\(a\) を求めよ。
(2) 正弦定理より
\(\displaystyle\frac{a}{\sin{45°}}\) \(=\) \(\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{6}}{\sin{60°}}\)
よって
\(\displaystyle a=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}\cdot\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{2\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=2\)
三角比10:余弦定理

\(a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\cos{A}\)
\(b^2=c^2+a^2-2ca\cos{B}\)
\(c^2=a^2+b^2-2ab\cos{C}\)
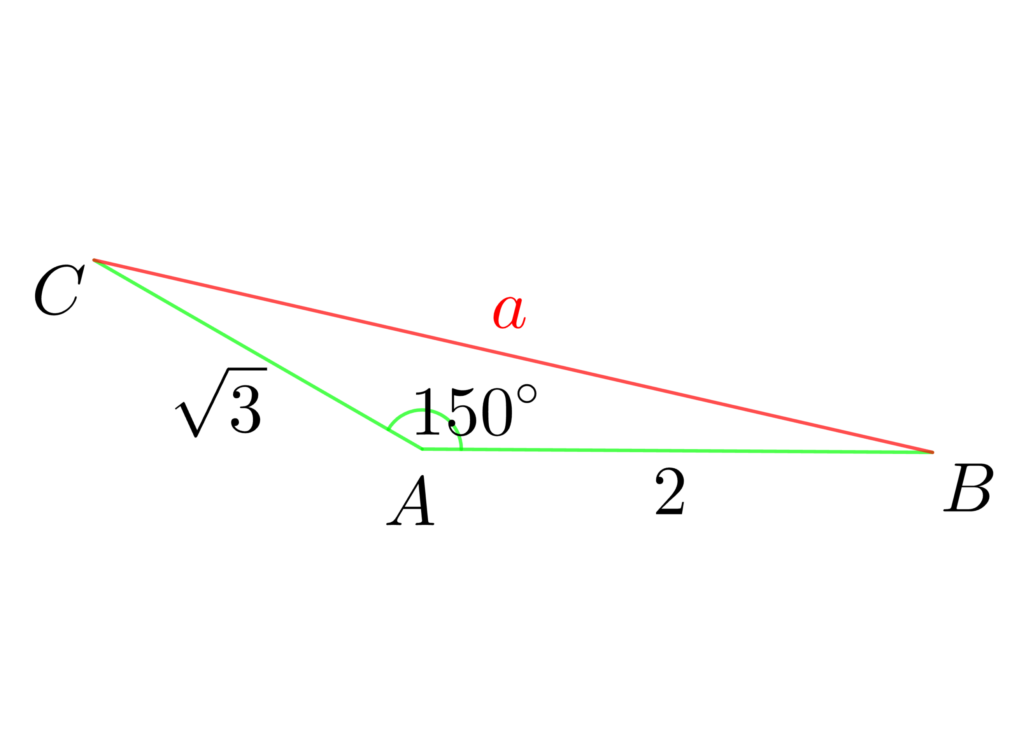
(1) △ABCにおいて、\(b=\sqrt{3}\) 、\(c=2\)、\(A=150°\) のとき、\(a\) を求めよ。
(1) 余弦定理より
\(\color{red}{a^2}=\color{lime}{{(\sqrt{3}\:)}}^2+\color{lime}{{2\:}}^2\)
\(-2\cdot\color{lime}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot \color{lime}{2}\cdot\color{lime}{\cos{150°}}\)
\(=3+4-2\cdot\sqrt{3}\cdot 2\cdot\left(-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\)
\(= 13\)
よって \(a>0\) より \(a=\sqrt{3}\)
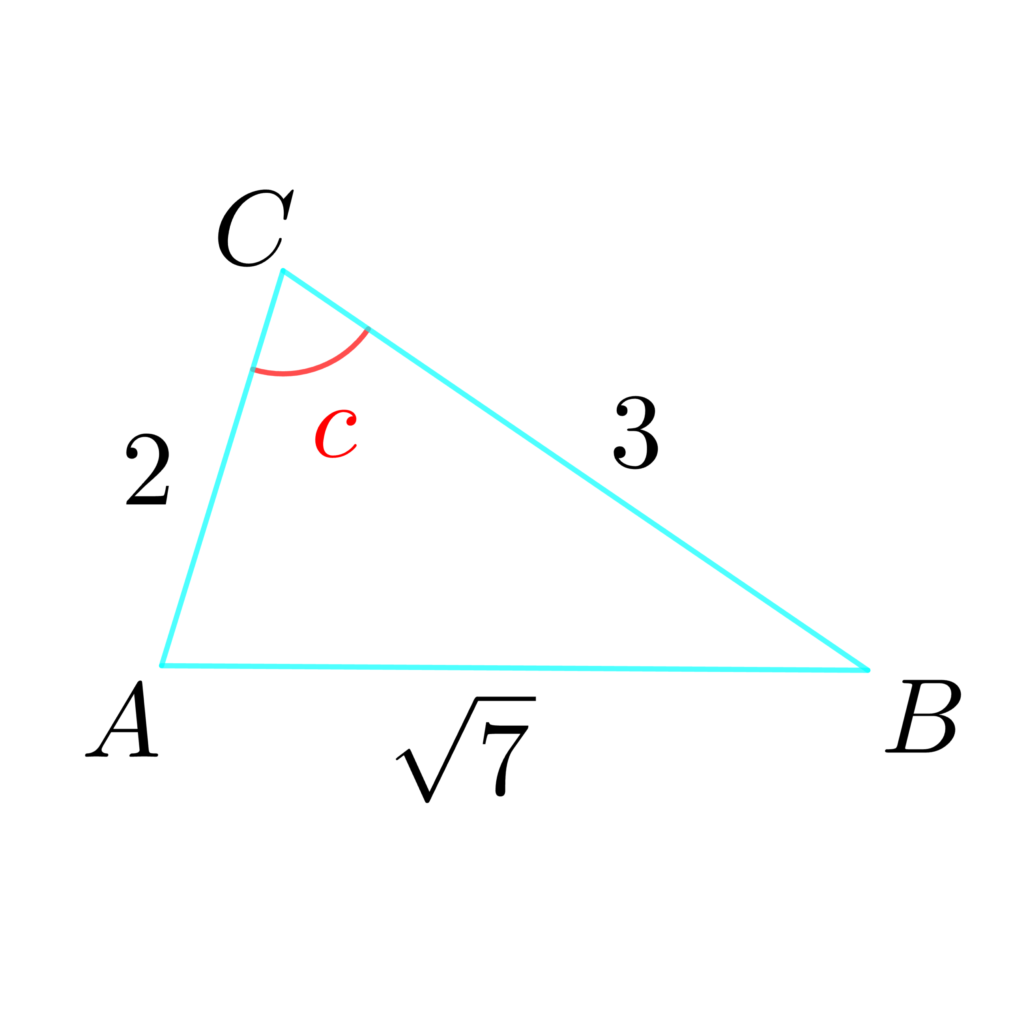
(2) △ABCにおいて、\(a=3\) 、\(b=2\)、\(c=\sqrt{7}\) のとき、\(C\) を求めよ。
(2) 余弦定理より
\(\displaystyle \cos{C}=\frac{\color{deepskyblue}{3}^2+\color{deepskyblue}{2}^2-(\color{deepskyblue}{\sqrt{7}})^2}{2\cdot \color{deepskyblue}{3}\cdot \color{deepskyblue}{2}}=\frac{1}{2}\)
よって
\(C = 60°\)
三角比11:正弦定理の比例式

正弦定理 \(\displaystyle\frac{a}{\sin{A}}=\frac{b}{\sin{B}}=\frac{c}{\sin{C}}\) は連比でも表せる
→ \(a:b:c=\sin{A}:\sin{B}:\sin{C}\)
☆ 比例式が与えられた場合、比率を文字で設定して通常の等式に変換する!
△ABC における次の等式が成り立つとき、この三角形の最大の角の大きさを求めよ。
\(\sin{A}:\sin{B}:\sin{C}=7:5:3\)
正弦定理より
よって、\(a=7k、b=5k、c=3k\) (\(k>0\)) とおける
また、最大辺は \(a\) であるから、最大角はAである
余弦定理より
よって、\(A=120°\)
三角比12:三角形の鋭角・直角・鈍角条件

Aが鋭角 \( \Leftrightarrow \cos{A}>0 \Leftrightarrow \) \(b^2+c^2-a^2>0\)
Aが直角 \( \Leftrightarrow \cos{A}=0 \Leftrightarrow \) \(b^2+c^2-a^2=0\)
Aが鈍角 \( \Leftrightarrow \cos{A}<0 \Leftrightarrow \) \(b^2+c^2-a^2<0\)
3辺の長さが \(a=9\), \(b=3\sqrt{2}\), \(c=7\) である△ABCは鋭角三角形・直角三角形・鈍角三角形のどれであるか。
\((3\sqrt{2})\:^2+7\:^2-9\:^2=-14<0\) より △ABC は 鈍角三角形
三角比13:三角比による三角形の面積

\(\displaystyle S=\frac{1}{2}bc\sin{A}\)
\(A=60°\), \(b=4\), \(c=3\), である△ABCの面積Sを求めよ。
三角比14:三角形の内接円の半径と面積

\(S=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}r(a+b+c)\)
- 他の方法で面積Sを求める
- \(S=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}r(a+b+c)\) を用いる
△ABCにおいて、\(a=5\), \(b=6\), \(c=7\) のとき、この三角形の内接円の半径 \(r\) を求めよ。
余弦定理より \(\displaystyle \color{red}{\cos{A}=\frac{{7}^2+{6}^2-{5}^2}{2 \cdot 7 \cdot 6}} = \frac{5}{7}\)
\(\sin{A}>0\) より \(\displaystyle \color{red}{\sin{A}=\sqrt{1-\left(\frac{5}{7}\right)^2}}=\frac{2\sqrt{6}}{7}\)
△ABCの面積をSとすると \(\displaystyle \color{red}{S=\frac{1}{2} \cdot 6 \cdot 7 \cdot \frac{2\sqrt{6}}{7}} =6\sqrt{6}\)
△ABC\(\displaystyle =\frac{1}{2}r(a+b+c)\)より \(\displaystyle 6\sqrt{6}=\frac{1}{2}r(5+6+7)\)
よって \(\displaystyle r=\frac{2\sqrt{6}}{3}\)


















コメント